Current affairs March 18-2021
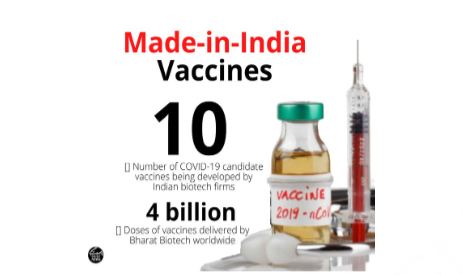
- “Made in India” Vaccines
- Country provides Made in India Vaccines for COVID-19 to 72 countries.
- Medicines have supplied to 150 Nations and 82 of them as grants.
- Vaccine Maithri – is an initiative launched by India to gift COVID-19 vaccines to neighboring countriesLaunched in January 20
- The COVID-19 vaccination programme started in India on January 16, 2021, with the two approved vaccines (Emergency use) – Covishield and Covaxin
- CovishieldDeveloped by the University of OxfordAlso known as AstraZeneca’s COVID-19 vaccineDCGI approved the emergency or conditional use of this vaccine on 1st January 2021.
- CovaxinDeveloped by Bharat Biotech in association with the ICMR and National Institute of Virology.First indigenous vaccine.DCGI approved the emergency or conditional use of this vaccine on 2nd January 2021.
- ICMR – Indian Council of Medical ResearchThe apex body in India for the formulation, coordination and promotion of biomedical research.ICMR is funded by Government of India through the Department of Health Research, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. The governing body of the council is headed by the Union Health Minister.
- DCGI – Drug Controller General of IndiaIs the head of department of the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization of the Government of India.DCGI is responsible for approval of licenses of specified categories of drugs .DCGI is under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.DCGI sets standards for manufacturing, sales, import, and distribution of drugs in India.The BrahMos sale to Philippines
- India and the Philippines signed the “Implementing Arrangement” for “procurement of defense material and equipment procurement”.
- Export of the BrahMos cruise missile, through the government-to-government route.
- BrahMos Cruise Missile
- Research began in late 1990s.
- Manufacture by BrahMos Aerospace Limited, a joint venture between the DRDO of India and the joint stock company Military Industrial Consortium NPO Mashinostroyenia of Russia.
- Capable of attaining a speed of Mach 2.8 (3 x speed of sound)
- Range of 400km
- Indian Navy inducted BrahMos in 2005 and Indian Army in 2007 and Indian Air Force in 2017 thus giving the missile a dominating presence in all three domains.
- A regiment of the BrahMos, including a mobile command post, 4 missile launcher vehicles, several missile carriers, and 90 missiles, reportedly costs around $275.77 million (Rs 2,000 crore).
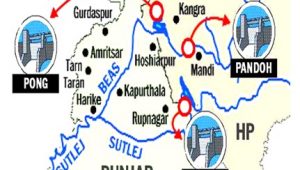
- Philippines becoming the 1st country to import the BrahMos
- Countries such as Vietnam, Philippines, Indonesia, The UAE, Argentina, Brazil, and South Africa have so far shown an interest in acquiring the systems.
- CAATSA – Countering America’s Adversaries Through Sanctions Act
- CAATSA is a United States federal law that imposed sanctions on Iran, North Korea, and Russia.
- It includes sanctions against countries that engage in significant transactions with Russia’s defense and intelligence sectors
- How it affects India?NPO Mashinostroyenia is one of the listed Russian entities. 65% of the components including the Ramjet engine and Radar seeker used in the BrahMos, are reportedly provided by NPO Mashinostroyenia.The export of the BrahMos may attract sanctions to India and the Importing Country.To not get sanctioned by CAATSA, countries may shy away from purchasing the BrahMos.India could also face USA sanctions for purchasing the S-400 Triumf missile defense system from Russia.
- Looking beyond privatization
- In the recent Budget session, the Union government announced its intent to privatize Public Sector Banks (PSBs).
- Improving efficiency has been citied the reason for this moveAround the world, innumerable private banks have failedIf private enterprises are the epitome of efficiency, why do private corporate entities have such large volumes of NPAs?Before bank nationalization in 1969, most banks were privately owned and they largely benefited the rich and powerful, neglecting the poor and vulnerable.
- The bank nationalization in 1969 and in 1980, transformed the banking sector, created jobs, extended credit to the agriculture sector and benefitted the poor.The move also helped in promoting more equitable growth, and this is evident from RBI data.It also improved the working conditions of employees in the banking sector.
-
- PSBs played a huge role in making the country self sufficient by supporting the green, blue, and dairy revolutions.
- Way ForwardStringent measures are required to recover large corporate stressed assets, which is a key concern for the entire banking sectorStrong recovery laws and taking criminal actions against willful defaulters.There is an urgent and imperative need to bring in a suitable statutory framework to consider willful defaults on bank loans a “criminal offence”.
- Appropriation Bill gets the nod of Lok Sabha
- Appropriation BillAlso known as supply bill or spending bill, is a proposed law that authorizes the expenditure of government funds.It is a bill that sets money aside for specific spending.In India an Appropriation Bill is a Bill that authorizes the government to withdraw funds from the Consolidated Fund of India for use during the financial year.
- The bill was passed after Speaker Om Birla put it through guillotine closure
- Guillotine Closure
- Guillotine is a closure motion moved by a member to cut short the debate on a matter before the house.A legislative mechanism to approve the fast-tracking of the passage of outstanding demands for grants without discussion
- Mission POSHAN 2.0
-
- Provides for testing of meals and food packets distributed at anganwadis for nutritional standards and quality by FSSAI Labs.
- The Poshan 2.0 Scheme will be an umbrella scheme covering the Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS), Anganwadi Services, Poshan Abhiyaan, Scheme For Adolescent Girls and National Creche Scheme.
- Poshan Abhiyaan is India’s flagship scheme to improve the nutritional outcomes of adolescents, children, pregnant women and lactating mothers.
- Ministry of Women and Child Development is the Nodal Ministry for implementing the mission POSHAN.
- POSHAN 2.0 scheme will be an umbrella scheme covering the ICDS (Integrated Child Development Scheme), Anganwadi Services, Poshan Abhiyan, Scheme for Adolescent Girls and National Creche Scheme.
- POSHAN – PM’s Overarching Scheme for Holistic Nourishment.
- POSHAN is with the mission with the vision to ensure attaining malnutrition free India by 2022.
-
- Mission POSHAN 2.0
- PSBs played a huge role in making the country self sufficient by supporting the green, blue, and dairy revolutions.
-