Current Affairs 29 March 2021
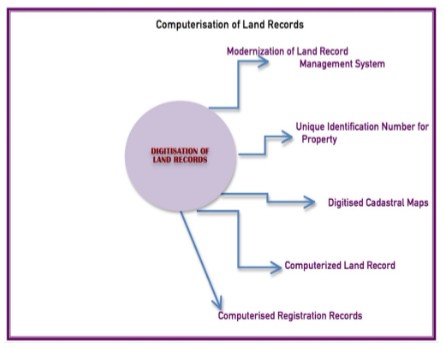
- Centre mulls unique ID for land by March 2022
- The centre plans to issue a 14 digit identification number to every plot of land in the country within a year.
- The Unique Land Parcel Identification Number (UL-PIN)
- The identification will be based on the Longitude and Latitude of the land parcel.
- Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP), 2008
- Integration of the Aadhaar numbers with the land record database would be done voluntary basis.
- These components will enhance the service delivery to the citizen of the country and will also function as input to the schemes of the other sectors like Agriculture, Finance, Disaster Management etc

- Digital India Land Records Modernization Programme (DILRMP), 2008
- The Land Reforms (LR) Division was implementing two Centrally Sponsored Schemes
- Computerisation of Land Records (CLR)
- Strengthening of Revenue Administration and Updating of Land Records (SRA&ULR).
- In 2008, the Cabinet merged the above two separate programs into Digital India Land Record Modernization Programme (DILRMP).
- Each District is taken as Unit of implementation, where all activities under the programme will converge.
- The Land Reforms (LR) Division was implementing two Centrally Sponsored Schemes
- Benefits to Citizens
- Real-time land ownership records
- Free accessibility to the records – reduced interface between the citizen and the government functionaries, thereby reducing corruption.
- Abolition of stamp papers and payment of stamp duty and registration fees through banks.
- Tamper proof records
- E-linkage to credit facilities
- Market value information will be available on the website to the citizen.
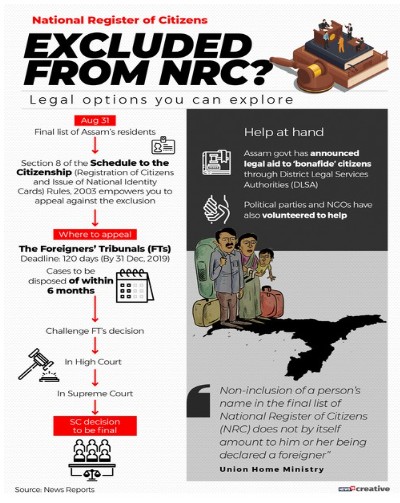
- NRC rejection, slips to be issued soon
- The Centre has told the Assam government that “rejection slips” to those excluded from the National Register of Citizens (NRC) published in 2019 should be issued immediately.
- Office of the Registrar General of India (RGI) under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) is the implementing agency.
- MHA had earlier said that “non-inclusion of a person in the NRC does not by itself amount to him/her being declared as a foreigner”.
- Non-included persons will be given adequate opportunity to present their case before the Foreigners Tribunals (FTs).
- The time limit to appeal before the FTs, the quasi judicial bodies unique to Assam, has been increased from 60 to 120 days.
- Assam is the only State where an NRC was compiled under the supervision of the top court.
- According to Article 6 of the Indian Constitution, the cut-off date for migration to India from Pakistan is July 19 1948, whereas according to the Assam Accord 1985, it is March 24, 1971.
- The BJP ruled Assam government has rejected the NRC in its current form and demanded re-verification of 30% names included in the NRC in areas bordering Bangladesh and 10% in remaining State.
- National Register of Citizens (NRC)
- NRC was 1st introduced after the 1951 Census of India
- The main purpose of NRC was the identification of illegal immigrants in Assam, who had migrated to Assam from Bangladesh during the 1971 war with Pakistan.
- This mass infiltration from the eastern border that are eroding the Assamese culture and changing the demographics of the region.
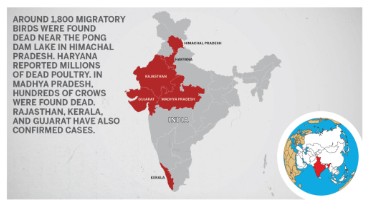
- 27 migratory birds found dead at wildlife sanctuary in Himachal
- Avian influenza in the Pong Dam Wildlife Sanctuary area of Himachal Pradesh.
- It could be avian influenza – H5N1 or H5N8 – waiting for the results to confirm it.
- Avian Influenza
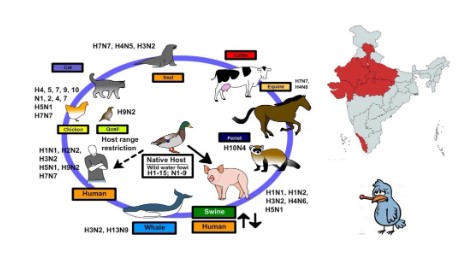
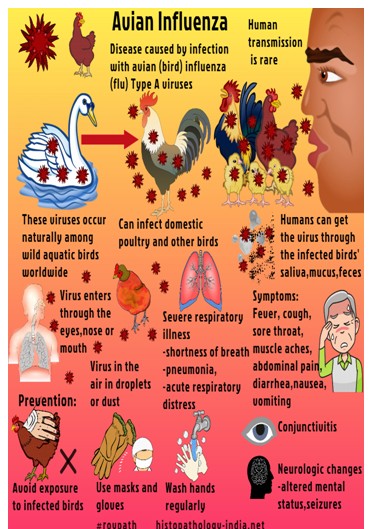
- Commonly known as Bird Flu, is a highly contagious viral disease affecting variety of birds.
- The frequent occurrences of bird flu cause a high degree of morality in birds and subsequent economic loss to the fast-growing poultry industry.
- There is also a risk associated with mutation of the virus and infection to the human.
- Source: Migratory birds from faraway countries in the northern hemisphere such as Mongolia and Kazakhstan are said to have brought the virus to India.
- The bird flu spreads through their droppings, contaminating the water bodies they visit.
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), more than half of the world’s bird flu incidents take place in the Central Asian Flyway (CAF), which covers almost the entire Indian subcontinent.
- Threat to Humans: The viral stain, H5N1 has a history of spreading over to humans from birds, but the instances of bird flu among humans are uncommon.
- Ebola and Nipha, both viruses are believed to be spread from birds to humans causing high casualty among humans.
- Pong Dam Wildlife Sanctuary
- Location: Kangra District, Himachal Pradesh.
- 1975 – Pong Dam was built across the Beas River, also known as Pong Reservoir or the Maharana Pratap Sagar.
- 1983 – The entire reservoir was declared as a Wildlife Sanctuary by the Himachal Pradesh government.
- 1994 – The Government of India declared it a “Wetland of National Importance”.
- 1992 – Pong Dam lake was declared as Ramsar Site

- India sends 2 lakh doses of vaccine to UNPKF
- United Nations Peace Keeping Force –UNPKF, received 2, 00,000 doses of COVID-19 vaccines.
- The cargo of AstraZeneca Covishield vaccines produced by the Serum Institute of India (SII) in Pune was sent despite the government’s decision to reduce exports in view of the need for vaccines domestically.
- India had thus far supplied more vaccines globally than have vaccinated our own people – India has exported 62 million doses of vaccines, while it has vaccinated about 55 million citizens, many of them whom have taken only the first dose.