Daily Current Affairs 24 March 2021
- As cases rise, govt. gives nod to inoculate all over 45 from April 1
-
- Citizens above the age of 45, irrespective of co-morbidity, will be eligible for COVID-19 vaccination from April 1.
- The Co-Win software is also being suitably modified for doing away with the need for confirmation of co-morbidities.
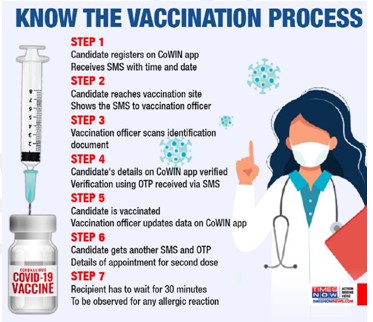
- Co-WIN
- Covid Vaccine Intelligence Network.
- Owned by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare.
- Was earlier the platform used for conducting Pulse Polio and other crucial immunization programmes across the country?
- The Co-WIN app is developed by the Ministry of Electronics and Information along with the National Informatics Centre by expanding the Co-WIN platform.
- This app would enable beneficiaries to be identified efficiently through use of Aadhaar platform.
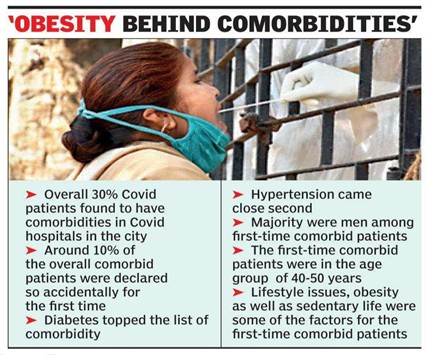
- Comorbidities
- The medical definition of Comorbidities is when a person has more than one underlying health-related conditions present in them at once. Each condition is considered as comorbidity, and sometimes Comorbidities could be present in the form of physical or mental conditions.
- The best example of Comorbidities are when a person is suffering from
- Asthma and Diabetes
- Depression and Hypertension
- Comorbidities that could put you at risk of contracting corona virus
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Cardiovascular diseases

- 2. Test, Track and Treat, MHA advises States
- Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) issued fresh COVID-19 guidelines, asking the state to strictly enforce the “test, track and treat” protocol
- Issued under the Disaster Management Act, 2005
- There shall be no restriction on inter-State and intra-State movement of persons and goods, including those for cross land-border trade under treaties with neighbouring countries
- No separate permission, approval or e-permit will be required for inter-State movement of passenger and goods
- Disaster Management Act, 2005
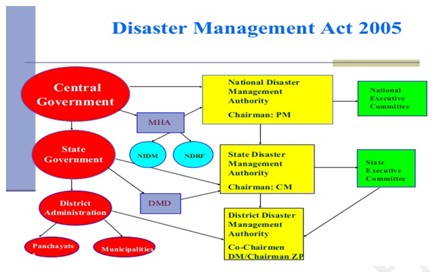
- The stated object and purpose of the DM Act is to manage disasters, including preparation of mitigation strategies, capacity-building, etc.
- It came to force in India in January 2006
- The Act calls for the establishment of National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), with the Prime Minister as chairperson
- All States are mandated to establish a State Disaster Management Authority
- Covid-19 is the first pan India biological disaster being handled by the legal and constitutional institutions of the country
- Under the Act, the States and Districts authorities can frame their own rules on the basis of board guidelines issued by the Ministry.
- India abstains in UNHRC vote on Sri Lanka
- The resolution on ‘Promoting reconciliation, accountability and human rights in Sri Lanka’ was, however, adopted after 22 states of the 47 member Council voted in its favour
- Why in news:
- Sri Lanka is facing a resolution calling on it to hold human rights abusers to account and deliver justice to victims of its 26-year civil war (1983-2019)
- The war was mainly a clash between the Sinhalese-dominated Sri Lankan government and the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) insurgent group, the latter of which had hoped to establish a separate state for the Tamil minority
- Sri Lankan forces and Tamil rebels were accused of atrocities during the war, which killed at least 1, 00,000 people.
- UNHRC’s Stand: The present government in Sri Lanka was “proactively” obstructing investigation and accountability, and that this had a “devastating effect” on families seeking truth, justice and reparations.
- India’s stand on pervious resolutions against Sri Lanka
- India voted against Sri Lanka in 2012
- India abstained in 2014
- India abstained in 2021
- HC grants cover to interfaith couple after attack
- Delhi High Court granted police protection to an interfaith couple
- The court provided police protection to them and the man’s family as after the attack they feel unsafe in their locality
- The man and the woman are consenting adults and got married of their own free will and their house was attacked by a mob of around 50 people
- Court has invoked Scheduled Caste and Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act.
- SC/ST Act, 2018
- It identifies specific crimes against Scheduled Cast and Scheduled Tribes as atrocities and describes strategies and prescribes punishments to counter these acts.
- The Act identifies what acts constitute atrocities and all offences listed in the Act are cognizable. The police can arrest the offender without a warrant and start an investigation into the case without taking any orders from the court.
- The Act also provides for the punishment for willful neglect of duties by non-SC/ST public servants.
- Quota percentage should be left to States, T.N. tells SC
- Tamil Nadu told a Constitutional Bench of the Supreme Court that the percentage of reservation should be left to the “subjective satisfaction” of Individual States.
- Tamil Nadu and Karnataka agreed with Maharashtra that 50% ceiling limit on reservation introduced in the Indira Sawhney Judgment by a nine-judge bench of the Supreme Court required a re-look.
- Indira Sawhney Judgment
- Indira Sawhney Vs Union of India 1992.
- Article 16 – the reservation in matters of Public Employment.
- The judgment recognized socially and economically backward classes as a category and recognized the validity of 27% reservation.
- The concept of “Creamy Layer” gained currency through this judgment.
- It laid down a 50% limit or upper ceiling on reservations.
- Reservations for backward classes should be confined to initial appointments and not extend to promotions.

Current Affairs 23 March 2021 | Shikara Academy
Tag: Current Affairs 24 March 2021 for Civils